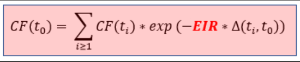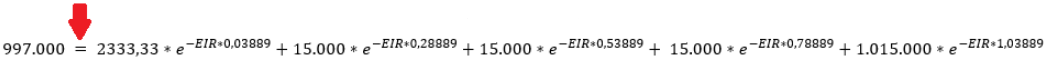The effective interest rate (EIR) is part of the effective interest method.T
The effective interest method is a method of allocating interest income or interest expense over the relevant period while calculating the amortised cost of a financial asset or a financial liability (or group of financial assets or financial liabilities).The EIR is the rate is the rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument or, when appropriate, a shorter period to the net carrying amount of the financial asset or financial liability.
In line with IFRS 9 "Appendix A Defined Terms", the computation of the effective interest rate is based on the expected cash flows of a financial instrument. The estimate of expected cash flows
- considers all contractual terms of the financial instrument, including but not limited to
- early repayment rights,
- calls,
- extensions
- and similar options
- but does not consider the expected credit losses.
The calculation includes all
- premiums, discounts
- transaction costs
- unwinding of the impairment adjustment
In general, the amortisation period is linked to the lifetime of the financial instrument. However, if a fee is only related to a shorter period, it is amortised over this period only.
For example, in the case of a financial instrument with a floating rate, the transaction price may contain premiums/discounts that reflect the current market situation. Hence, the premiums/discounts related to the current market rate will be amortised only over the current fixing period. Instead, if the premiums/discounts are linked to a change in credit spread or other variables that are not related to the market rate, it will be amortised over the lifetime of the financial instrument.
The effective interest rate (EIR) for a deal is calculated using the following formula:
With
CF(t0) represents the initial cash flows for the deal (i.e. the outpayment of the nominal amount by the bank plus/minus possibly arising transaction costs, premiums/discounts or upfront payments),
CF(ti) stands for the cash flows for the deal at further payment dates ti
Δ(ti,t0) is the time gap between payment date ti and deal origination date t0.
...
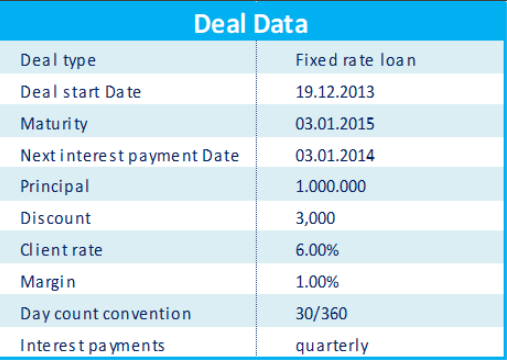
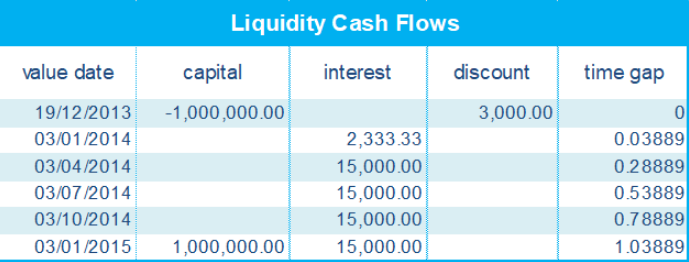
Hence, the following cash flows are relevant:
Using the EIR formula shown above, the following equation is considered:
Solving the equation leads to an approximated value for EIR = 6.45264%.The effective interest method is basis for financial instruments measured at amortised cost. It s a method of allocating interest income or interest expense over the relevant period while calculating the amortised cost of a financial asset or a financial liability (or group of financial assets or financial liabilities).
Please refer to the section below for further details about:
| Children Display |
|---|